Abstract
Light field images contain both angular and spatial information of captured light rays. The rich information of light fields enables straightforward disparity recovery capability, but demands high computational cost as well. In this paper, we design a lightweight disparity estimation model with physical-based multi-disparity-scale cost volume aggregation for fast disparity estimation. By introducing a sub-network of edge guidance, we significantly improve the recovery of geometric details near edges and improve the overall performance. We test the proposed model extensively on both synthetic and real-captured datasets, which provide both densely and sparsely sampled light fields. Finally, we significantly reduce computation cost and GPU memory consumption, while achieve comparable performance with state-of-the-art disparity estimation methods for light fields.
Method
We propose FastLFnet, a fast light-field disparity estimation network which can not only produce accurate estimations, but also significantly speed up inference. We design an edge guidance sub-network to guide the disparity estimation with edge cues for better performance on challenging regions. Specifically, we propose to extract edge features with the edge feature extraction (EFE) module from the center view image and the extracted edge feature maps are then integrated into a pixel-wise edge feature fusion (EFF). To aggregate the cost volume from different views, we propose a layer-by-layer multi-disparity-scale cost aggregation (MCA) architecture to integrate pyramid cost volumes for fast and high performance cost volume regularization. The method achieves competitive performance with the state-of-the-art methods with much faster computing speed and lower GPU memory comsumption.
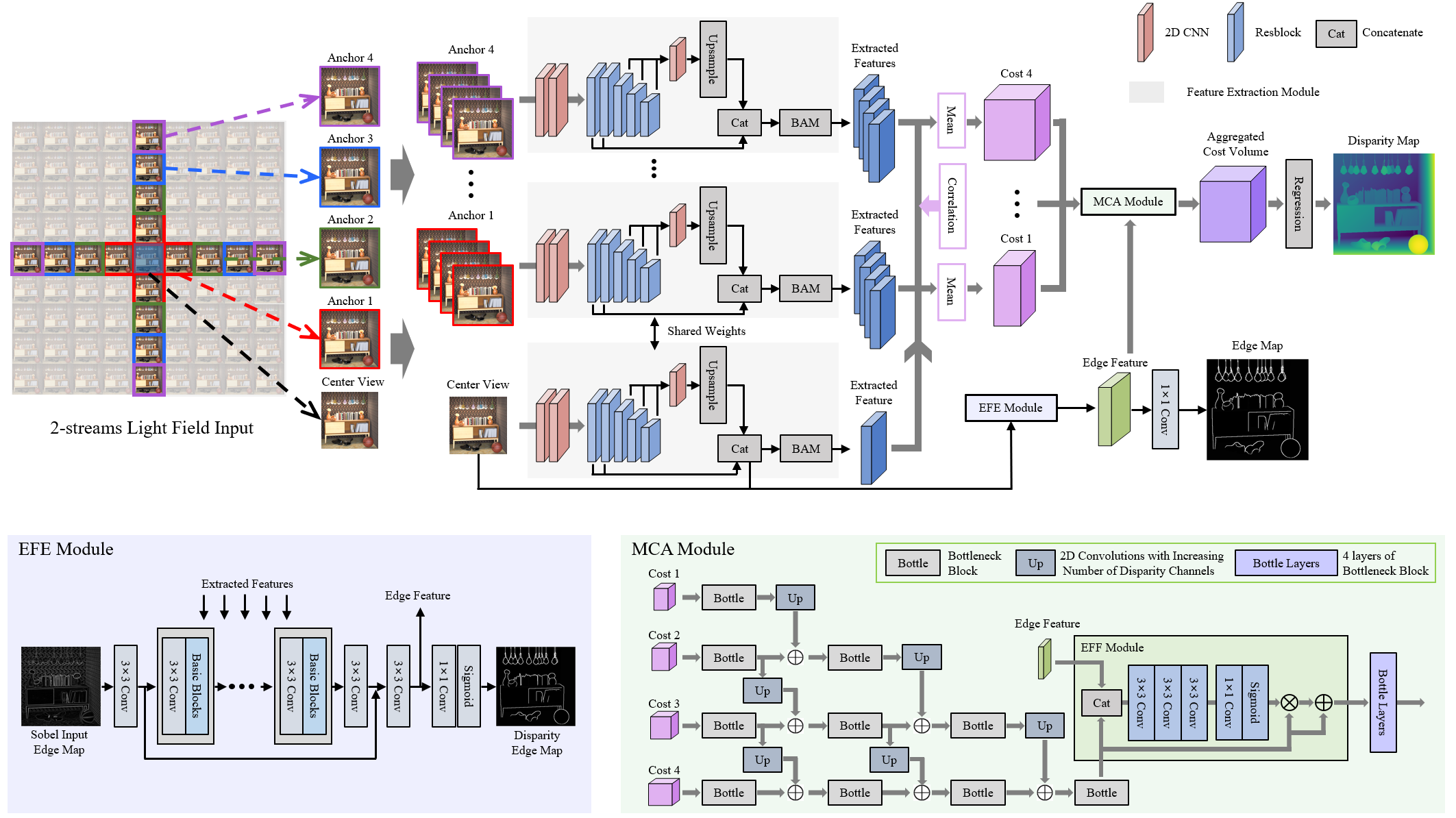
Figure 1. Overview of the proposed FastLFnet. The overall FastLFnet is at the top right of the figure.
Experiments
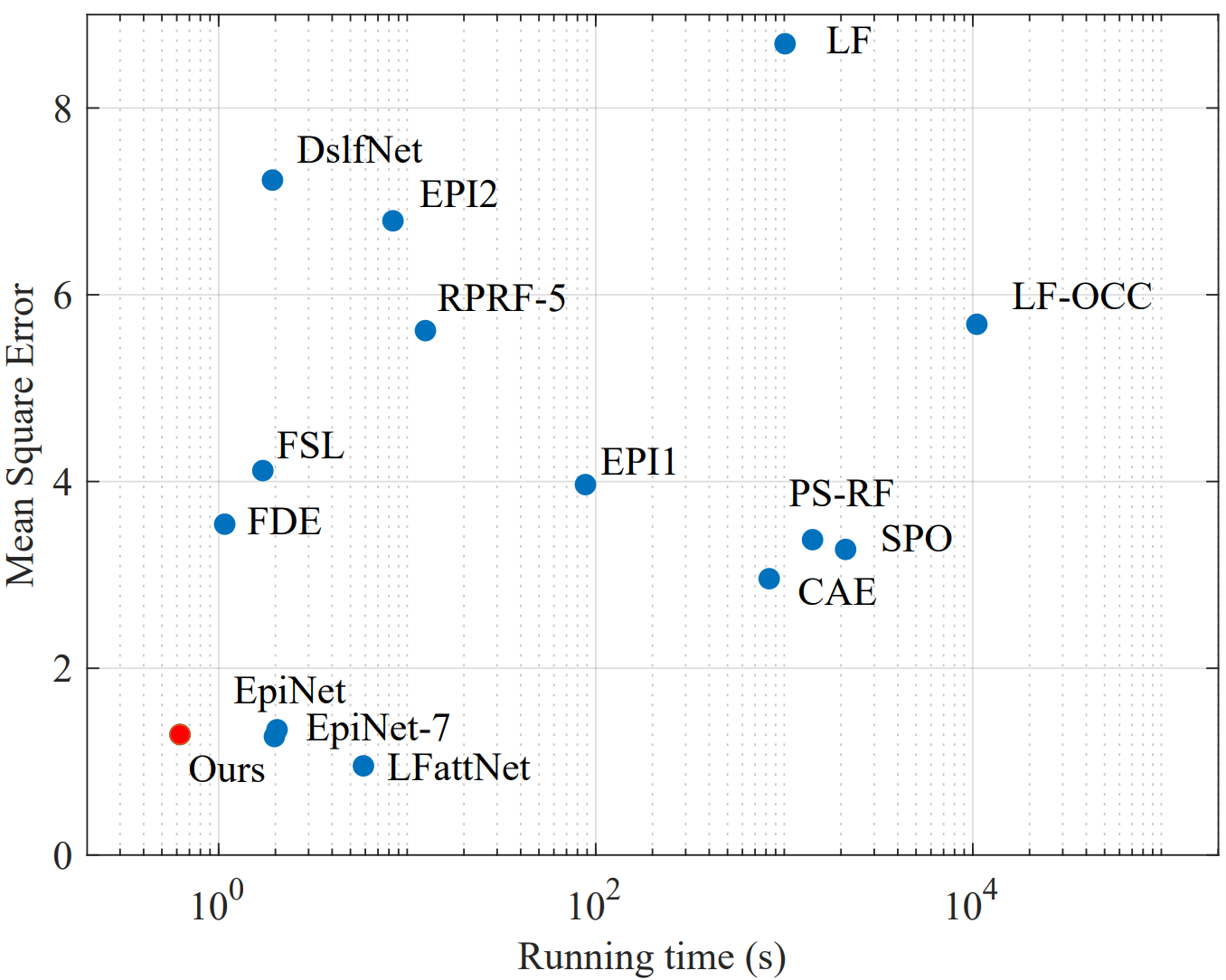
Figure 1. Comparison in performance and efficiency of light field disparity estimation algorithms on the 4D light field dataset.
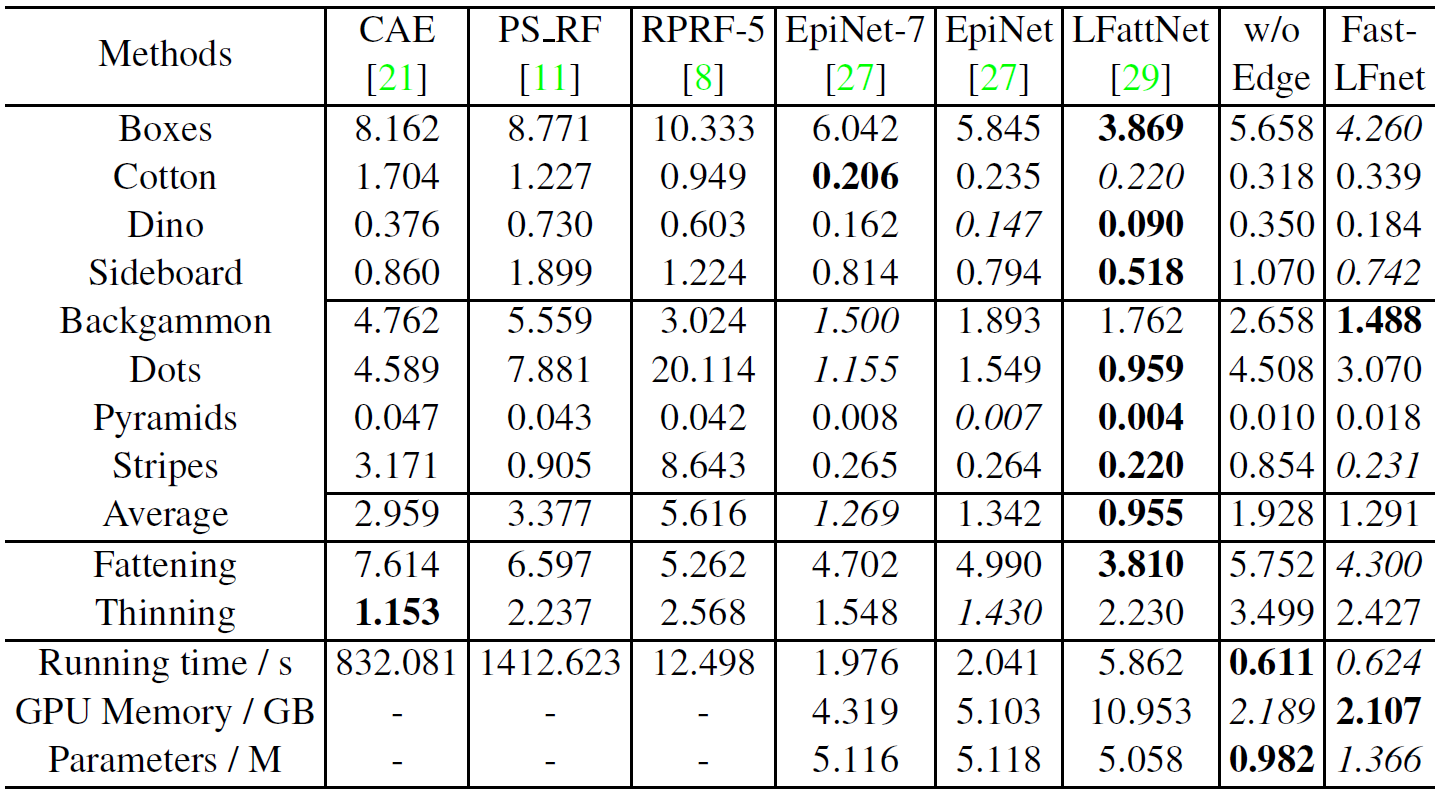
Table 1. Quantitative comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on the 4D Light Field Dataset.
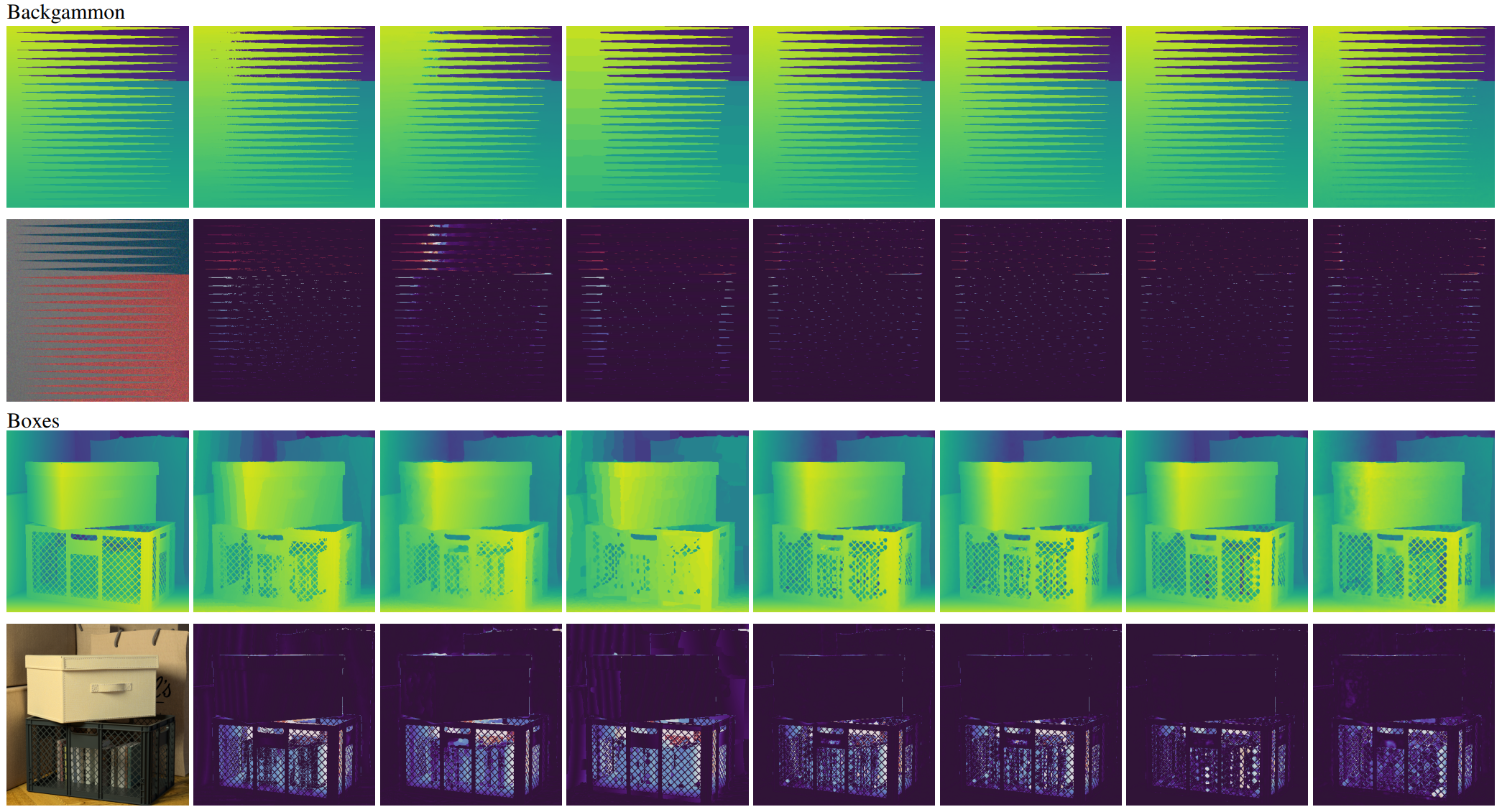
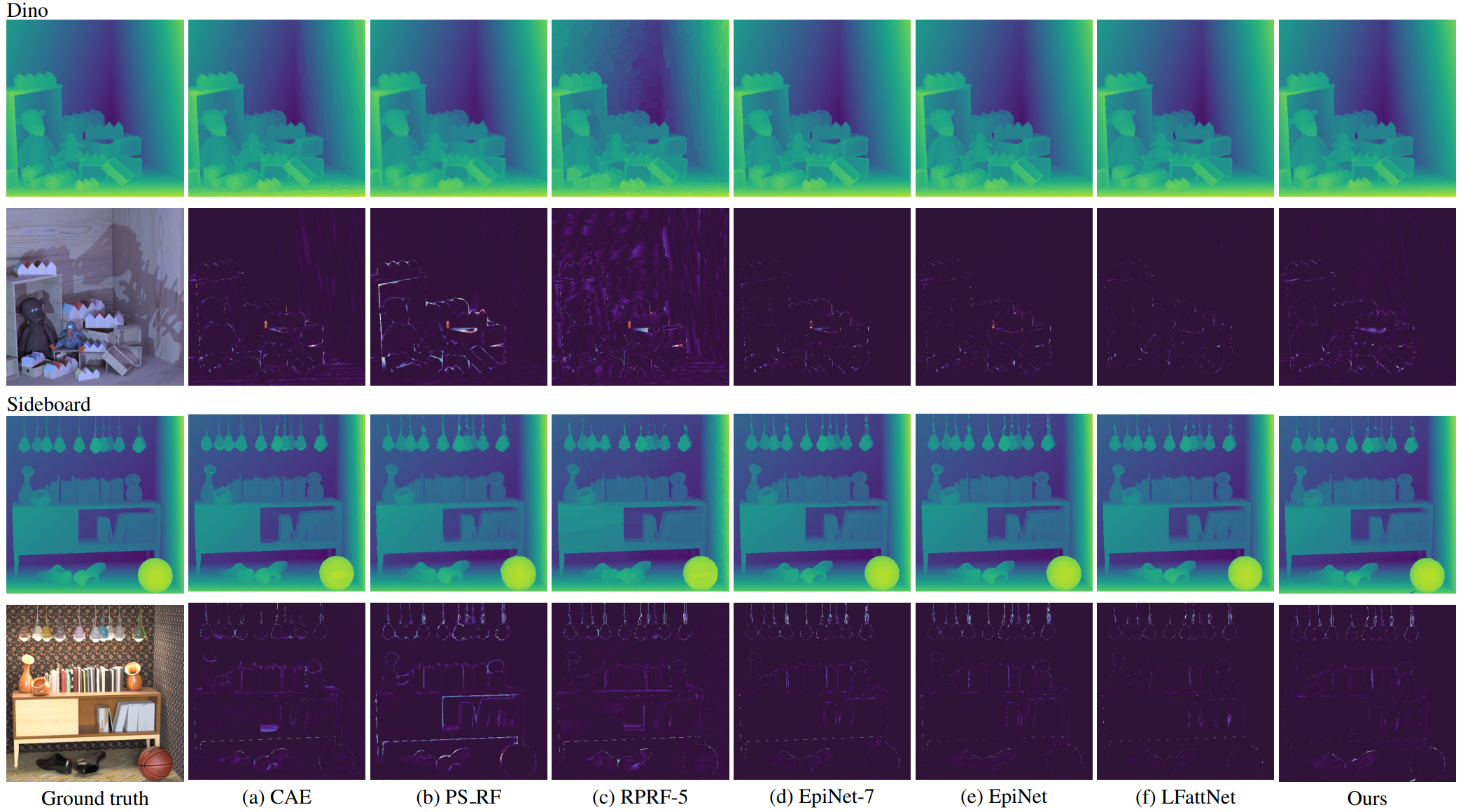
Figure 2. Qualitative results of our method and other compared methods on the 4D light field dataset.
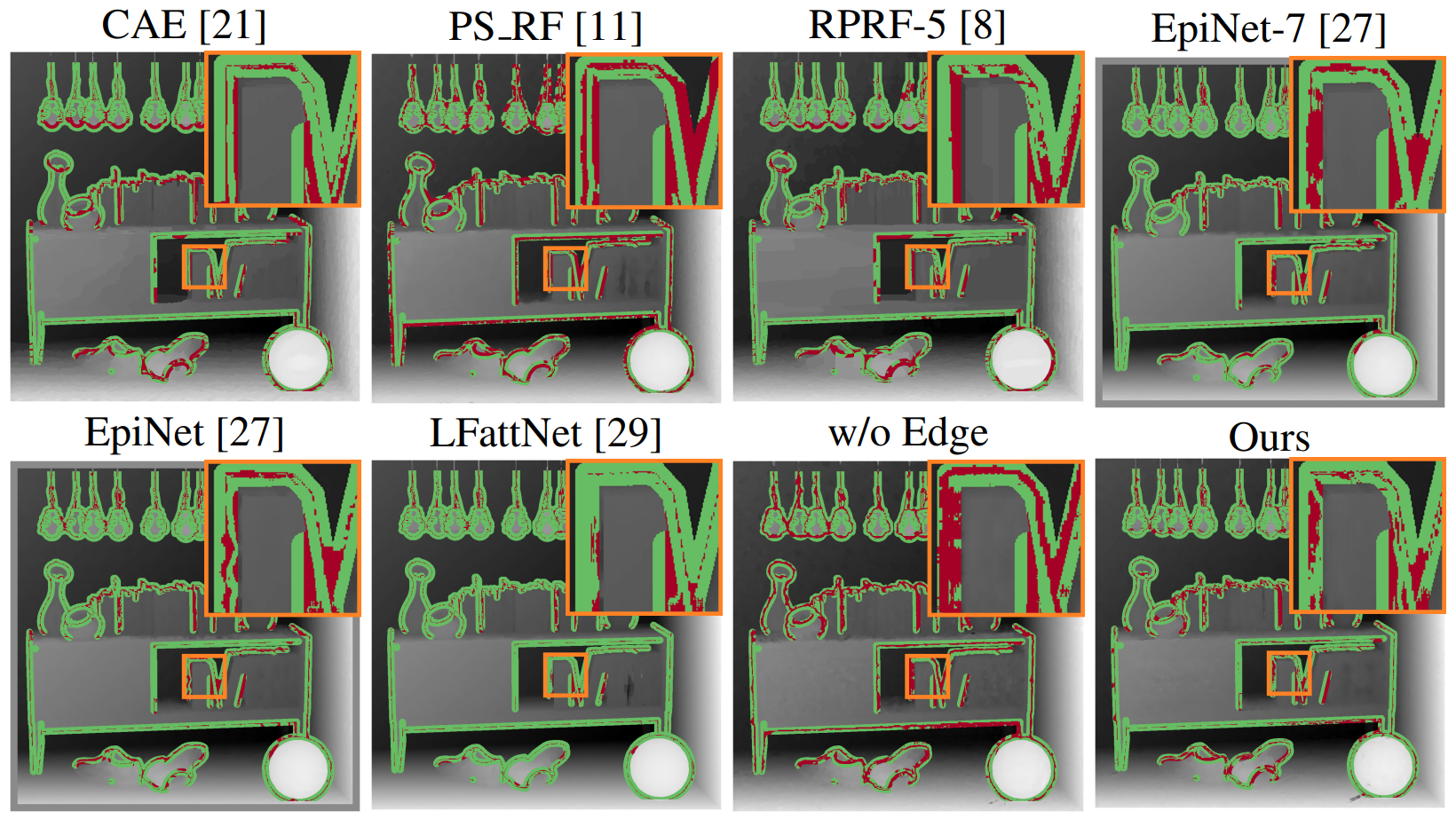
Figure 3. Error maps of Discon BadPix for the scene Sideboard on the 4D light field dataset.
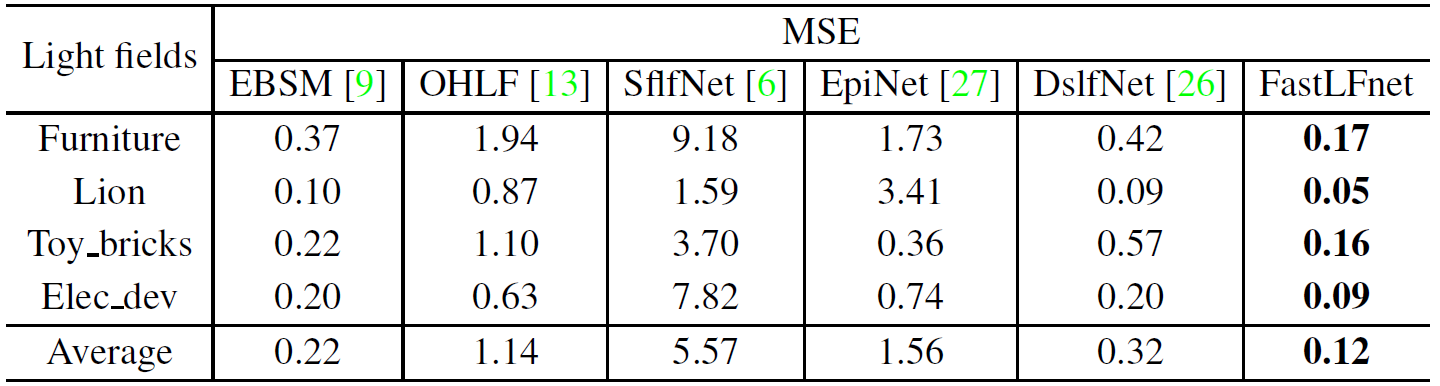
Table 2. Results of the performance comparison on the Sparse Light Field Dataset in terms of MSE.
More Details
- File
- Presentation
- Dataset: 4D light field dataset
- Available source code: GitHub
Bibtex
@InProceedings{huang2021fast,
title = {Fast Light-Field Disparity Estimation With Multi-Disparity-Scale Cost Aggregation},
author = {Huang, Zhicong and Hu, Xuemei and Xue, Zhou and Xu, Weizhu and Yue, Tao},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
pages={6320--6329},
year = {2021}
}